Riku Kiviluoto
Doctoral Researcher
Cardiometabolic research
A.I. Virtanen Institute for Molecular Sciences, Faculty of Health Sciences
Cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) remain the primary cause of morbidity and mortality worldwide, accounting for 18.6 million deaths annually. The World’s leading cause of hospitalization is heart failure (HF), affecting over 64 million people worldwide. Coronary artery disease (CAD) is one of the CVDs and it can lead to HF. CAD is caused by plaque building up in the wall of the coronary arteries which narrows arteries over time. This process is called atherosclerosis. Despite significant medical advances, HF has no cure.
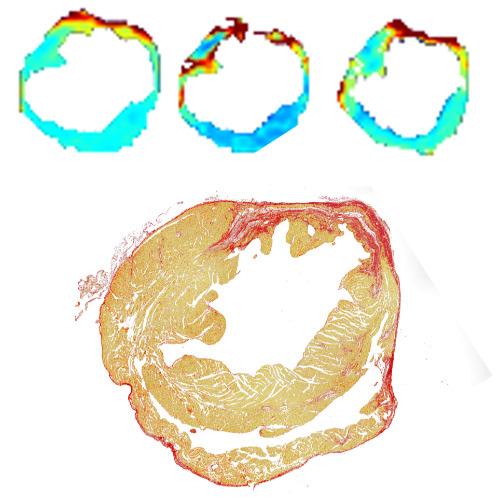
Non-invasive imaging methods such as positron emission tomography (PET), magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and computed tomography (CT) have the potential for early detection of HF with CAD. These imaging modalities provide detailed information on anatomical, functional and metabolic aspects of the cardiovascular system, which can help to identify individuals at risk and potentially prevent the progression of HF. Timely diagnosis and intervention reduce the morbidity and mortality associated with HF.
Current imaging techniques for myocardial inflammation have limited specificity. New approaches using PET/MRI techniques are needed for more specific and early detection of myocardial inflammation.