
FOODNUTRI - Climate Smart Food and Nutrition Research Infrastructure
Funders


FOODNUTRI has missions to:
- provide know-how including tools and methods on food characteristics, physiological responses to food, consumer acceptance, food consumption and nutrient intake of populations as well as on environmental and health impacts
- strive in developing tools and databases for high quality support and services for maintaining the dietary research infrastructure, assessing environmental burden of our diets, and developing modelling tools and services for dietary risk assessment and monitoring based on versatile channels of food information
- upgrade domestic raw materials and explore agricultural and other side-streams for production of foods and food ingredients by exploiting sustainable food processing technologies
- enhance and strengthen regional expertise and develop the research and innovation platform as part of the national research infrastructure
- develop the research platform as open service based products
We will set up and validate methods to support research related to food microbiological safety, in vitro dynamic gastrointestinal model, advanced analytics, and digital measuring methods of food consumption and quality of diet. Additionally, we will develop a digital feedback application.
Cooperation
-
Marina Heinonen
-
Niina Kaartinen
-
In vitro modeling of gut microbes and gut barrier function is part of the FOODNUTRI “Physiological responses to food” research platform. The platform’s overall objective is to ensure population health by generating high-quality evidence on the physiological responses driven by foods, food components, and diets, thereby promoting the adoption of nutritious diets.
The well-being of the gut microbiota and gut barrier plays a crucial role in maintaining health, influencing the development of diseases, and preventing them. The abundance and diversity of gut microbiota have been linked to various conditions, including low-grade inflammation, cardiovascular diseases, type 2 diabetes, cancers, and allergies. The quality of food and diet significantly impacts the composition of the gut microbiota and the well-being of the gastrointestinal wall. A diet rich in fiber, such as whole grains, vegetables, berries, and fruits, promotes a diverse microbiota, supports the well-being of the intestinal wall, and reduces its permeability.
Within the FOODNUTRI project, we are further developing the in vitro intestinal model. During the project we have established a modular gastrointestinal model that can be connected to a new module featuring human cell cultures (picture 1). This setup allows us to study the effects of metabolites from digestion and/or the microbiota on human tissues, including the intestinal barrier. The piloting of the new module involves existing and new food products or their raw materials, with a particular focus on their impact on human microbiota composition and activity, and intestinal permeability.
By employing in vitro modeling, we can comprehensively investigate the effects of foods and their components in the gut. The insights obtained from the model can be combined with information from meal studies. This evidence-based platform’s development enables a profound understanding of the mechanistic effects of food, offering significant potential for individual health maintenance and disease prevention in the future. The modular gut model can be utilized to determine the health effects of foods or their components at an early stage of food development. In vitro modeling also allows the study of the intestinal-mediated health effects of novel food sources or components before they can be tested in humans, contributing to our understanding of their effects from both health and safety perspectives.

Picture 1. Modular in vitro gastrointestinal model.
-
Clinical meal studies are part of the FOODNUTRI ’Physiological responses to food’ -research platform. The overall objective of the platform is to secure population health through ensuring adoption of nutritious diets by generating high-quality evidence on the physiological responses driven by foods, food components and diets.
Clinical postprandial studies are for exploring human metabolic effects of foods right after the meal.
Postprandial i.e. meal studies are part of the long tradition of clinical food and dietary intervention studies done at the Institute of Public Health and Clinical Nutrition. Meal studies are conducted with very different approaches and various scientific views to understand acute food related glucose and lipid metabolism, inflammation as well as related satiety and hunger responses, attitudes, sympathetic and parasympathetic responses, and brain activities.
FOODNUTRI-project aims to design a meal study service concept that takes flexibly into account various stakeholder needs. Service design will be formulated using pilot studies with several different foods or food components as an effector.
The approaches and aims of meal studies are flexible modifiable. Additionally, volunteers to recruited to participate in the meal study can be chosen to represent various population groups based on the study question and aim. There is also a possibility to add short term intervention to be connected with a meal study if the interest is in how the intervention can have an effect on the meal responses. The challenge when planning the meal study is to find a suitable control product. This is very important, because the study question and control product will determine which question(s) the meal study is able to answer. Thus, it is important to know the literature around the chosen approach and to openly discuss on the needs and questions for which the meal study is done.
-
Promoting Digital Nutrition Tools in Collaboration with the Regional FOODNUTRI Project in North Savo
Together with the regional FOODNUTRI project in North Savo, we advance the development of national digital apps for measuring individual food consumption and providing automated, personalized dietary feedback. This initiative supports the infrastructure for nutrition research.
Online Nutrition Tools to Support Public Health and Research
By utilizing online nutrition tools, we aim to improve individuals’ and populations’ nutritional health, enhance well-being, and promote sustainable food consumption. This, in turn, can help prevent chronic diseases. To strengthen regional and national opportunities for improving nutritional health and conducting nutrition research, we have developed digital methods for measuring food consumption and a personalized feedback system.
The online tool developed to measure dietary quality in this project is called Ravitsemusnavigaattori (Finnish Nutrition Navigator), supported by the Ravitsemuspolku (Finnish Nutrition Path) website, which provides additional guidance and tips for dietary changes. Through Ravitsemusnavigaattori, individuals can assess their diet against national nutrition recommendations and receive automated, personalized dietary feedback that encourages healthier eating habits. The web-app is based on the scientifically evaluated Healthy Diet Index, which was originally developed in type 2 diabetes prevention studies. Experts in nutrition science from multiple organizations, including the University of Eastern Finland, Savonia University of Applied Sciences, and the Finnish Institute for Health and Welfare, have contributed to its development.
Online Tools Are Currently Being Tested and Researched
The online tools have been developed in collaboration with Savonia University of Applied Sciences. We have tested them with both consumers and professionals and are integrating them in cooperation with local businesses, the City of Kuopio, sports instructors in North Savo, occupational healthcare services, and other stakeholders. Currently, the usability and effectiveness of these tools are being piloted and evaluated within occupational healthcare services and lifestyle coaching by sports instructors.
Ravitsemusnavigaattori provides a measure of dietary quality, which can be used for structured documentation in healthcare or as an indicator in research on dietary changes. The tools are also being developed to support researchers in dietary data collection and monitoring. We conduct extensive research collaborations, and the project generates valuable insights into the applicability and impact of these tools in various environments and use cases.
In Figure 1 below, the development phases of the Ravitsemusnavigaattori web app in the FOODNUTRI regional project in North Savo are illustrated.
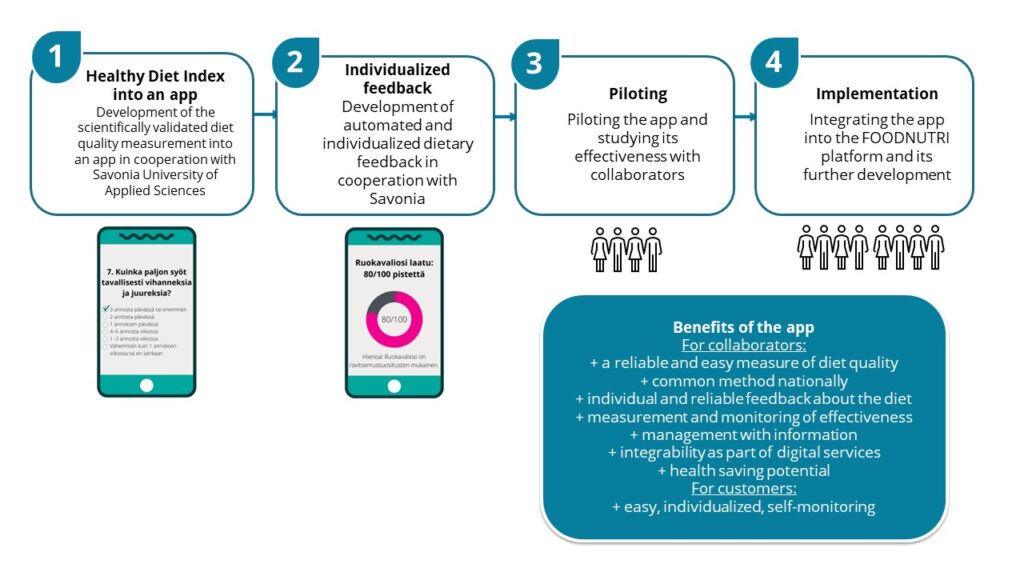
Figure 1. Development of the Ravitsemusnavigaattori web app in the regional FOODNUTRI project. Regarding the development and use of the Ravitsemusnavigaattori web app, please contact the researchers Kirsikka Aittola, Maria Lankinen or Elina Järvelä-Reijonen from the University of Eastern Finland.
Explore Ravitsemusnavigaattori here.
Explore Ravitsemuspolku here.
Watch the introductory video on online nutrition tools below (in Finnish):
-
The controlled extension of the shelf-life of food products aligns with global objectives of resource efficiency, reducing food waste, and promoting self-sustainability. Achieving this requires high-quality raw materials, as well as studied and optimized food processing methods.
Research facilities for studying food microbiological quality is a key element of the FOODNUTRI research platform. In addition to traditional food microbiology methods, we utilize more convient and faster methods for identifying food pathogens and spoilage microbes.


The Tempo and MiniVidas equipments can be used to analyse wide range of food pathogens and spoilage microbes from food samples.
Food microbiology methods can be used in shelf life tests, e.g. to study the effects of various food processes such as freeze drying.

With the Leo-004 freeze dryer, you can freeze dry foods and raw materials, test the suitability of various foods for freeze drying process, and study the effect of the process on the shelf life and quality of food.
Professors
Senior Researchers
-

Carlos Gomez Gallego
University LecturerInstitute of Public Health and Clinical Nutrition, School of Medicine, Faculty of Health Sciences -

Maria Lankinen
University LecturerInstitute of Public Health and Clinical Nutrition, School of Medicine, Faculty of Health Sciences -

Anu Ruusunen
Clinical LecturerInstitute of Public Health and Clinical Nutrition, School of Medicine, Faculty of Health Sciences -

Otto-Ilari Savolainen
Senior ResearcherInstitute of Public Health and Clinical Nutrition, School of Medicine, Faculty of Health Sciences -

Jenni Korhonen
Senior University LecturerInstitute of Public Health and Clinical Nutrition, School of Medicine, Faculty of Health Sciences
Post-doctoral Researchers
-

Elina Järvelä-Reijonen
Postdoctoral ResearcherInstitute of Public Health and Clinical Nutrition, School of Medicine, Faculty of Health Sciences -

Kati Väkeväinen
University LecturerInstitute of Public Health and Clinical Nutrition, School of Medicine, Faculty of Health Sciences -

Kaisa Raninen
Postdoctoral ResearcherInstitute of Public Health and Clinical Nutrition, School of Medicine, Faculty of Health Sciences
Doctoral Researchers
-

Kirsikka Aittola
Doctoral ResearcherInstitute of Public Health and Clinical Nutrition, School of Medicine, Faculty of Health Sciences -

Moona Partanen
Doctoral ResearcherInstitute of Public Health and Clinical Nutrition, School of Medicine, Faculty of Health Sciences -

Johanna Mylläri
Project ResearcherInstitute of Public Health and Clinical Nutrition, School of Medicine, Faculty of Health Sciences
Technicians
Research Nurses
Research trainee
Other group members
Publications
2 items-
Proteiinien sulavuus ja kestävyysparadoksi: kasvipohjaisten ruokavalioiden tulevaisuus
Partanen, Moona, 2024, Ravitsemusasiantuntija, 10, 2, 8-10. D1 Article in a trade journal -
The role of fiber in modulating plant protein-induced metabolic responses
Partanen, Moona; Luhio, Petri; Gómez-Gallego, Carlos; Kolehmainen, Marjukka, 2024, Critical reviews in food science and nutrition, 65, 23, 4599-4614. A2 Review article, Literature review, Systematic review


